Essential Guide to XBRL Reporting for ACRA Filing in Singapore: Tips and Best Practices for Efficient Reporting
Businesses in Singapore must prepare their financial statements in XBRL reporting format for submission to ACRA (Accounting and Corporate Regulatory Authority). It includes a complete set of financial statements, a reduced set of financial statements, or financial statement highlights. Companies, corporate secretaries, accountants and other XBRL preparers will benefit from this.
Additionally, it provides background information that is helpful to developers who are designing XBRL software so that it complies with ACRA Taxonomy 2016 or 2020 filing standards.
ACRA Taxonomy is a closed taxonomy that does not permit preparers to add or define company-specific concepts or create linkages. To give preparers flexibility in their presentation, the taxonomy still permits some customisations, such as company-specific labels and idea reordering.
Some Tips and Best Practices for the XBRL Reporting with ACRA Filing:
It can be challenging to navigate Singapore’s ACRA XBRL reporting system. However, with the correct advice and best practices, you can make it easier while ensuring regulatory compliance. Some tips and practices that must always be taken into consideration are:
- Understand the Filing Requirements: Financial reporting is standard XBRL format. Financial statements are created using this format and sent to ACRA. Find out if your business needs to submit financial statements in XBRL format. This rule may not apply to all businesses, and the standards may evolve.
- Prepare Financial Statements by Guidelines: The Singapore Financial Reporting Standards (SFRS) or the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) must be followed while preparing your financial accounts. Get the most recent XBRL taxonomy 2022V1.0 from the ACRA website. This taxonomy defines the specific data components and reporting specifications.
- Close Monitoring: Use the XBRL solutions to map and tag each data point in your financial statements to the appropriate element in the taxonomy. Make sure your tagging is accurate and consistent. Create the XBRL files per ACRA’s specifications after your financial statements have been appropriately tagged and authenticated.
- Maintain Records: Keep track of your XBRL filings and the supporting paperwork for the duration specified by ACRA. Check the ACRA website and communications frequently for updates, modifications to the rules, or additions to the XBRL filing system.
Ensuring Flawless XBRL Reporting Compliance with ACRA Filing
Filing financial statements with ACRA using XBRL format is a critical process for companies in Singapore. While this process enhances transparency and efficiency in financial reporting, it’s fraught with potential errors that can complicate compliance efforts. Below are detailed insights into common mistakes and how to avoid them for successful XBRL ACRA filings.
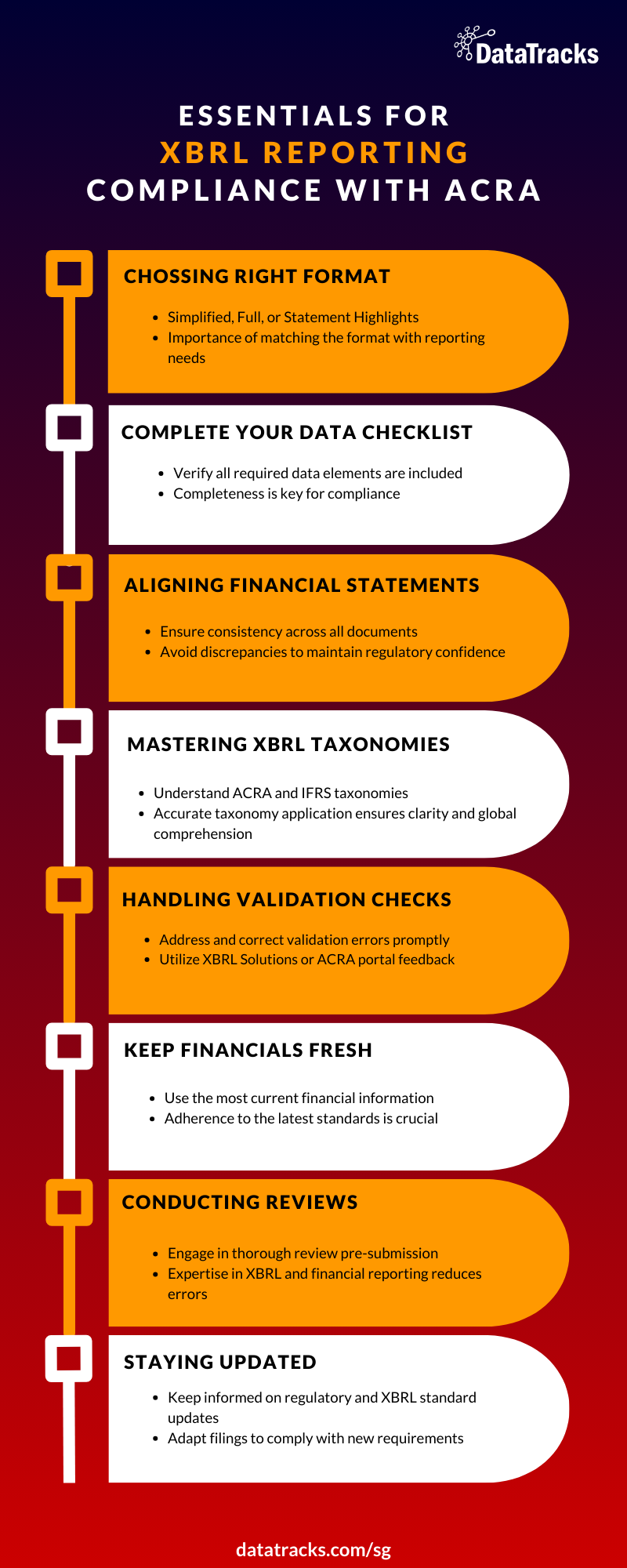
Understanding the Right XBRL Reporting Format
Selecting the correct XBRL format—Simplified, Full, or Statement Highlights—is crucial. Mistakes in format selection can lead to unnecessary complications or compliance issues, highlighting the importance of comprehending each format’s specific application.
In Singapore, selecting the appropriate XBRL format—be it Simplified, Full, or Statement Highlights—is vital. Choosing incorrectly can introduce unnecessary challenges or result in compliance dilemmas, emphasizing the significance of understanding the specific application of each XBRL format type. This decision impacts the precision and effectiveness of financial reporting to ACRA, showcasing the need for businesses to familiarize themselves with the nuances of each format.
Ensuring Comprehensive Information Reporting
A common error is the omission of required data elements. Completeness of information is non-negotiable for XBRL ACRA filings, necessitating meticulous review and confirmation of all data prior to submission.
Aligning XBRL Data with Financial Statements
Discrepancies between XBRL filings and other financial statements (e.g., PDFs) can trigger regulatory scrutiny. It’s imperative to maintain consistency across all submitted documents for regulatory compliance and to uphold stakeholder confidence.
Mastering XBRL Taxonomies
Navigating XBRL filings means getting cozy with some pretty specific rules, kind of like learning the rules of a new board game. Think of taxonomies as the rulebook. There’s one for ACRA, which is like the local guide for Singapore, making sure all the financial info speaks the same language as the Accounting and Corporate Regulatory Authority expects. Then, there’s the IFRS Taxonomy, which is more like the international rulebook, used by companies that play on the global stage to ensure their financial reporting can be easily understood worldwide.
Getting these taxonomies right is super important. Imagine playing that board game but mixing up the rules — things can go sideways pretty fast. The same goes for XBRL filings. Knowing your way around both the ACRA and IFRS taxonomies isn’t just about avoiding mistakes; it’s about making sure your financial reporting is as clear and accurate as a sunny day in Singapore, whether you’re talking to local regulators or an international audience.
Addressing Validation Checks
Validation errors, if ignored, can prevent successful submission. Attentive correction of validation errors based on XBRL software or ACRA’s portal feedback is essential for error-free filings.
Keeping Financial Data Current
Submitting outdated financial statements is a significant error. It’s essential to ensure that filings reflect the latest financial data, compliant with current accounting standards and regulatory requirements.
Conducting Thorough XBRL Reviews
Insufficient review of XBRL documents before submission can lead to errors. Engaging individuals with XBRL and financial reporting expertise for document review can mitigate this risk.
Staying Informed on XBRL Changes
Regulatory and XBRL reporting standards are subject to change. Staying abreast of ACRA’s updates and modifying filings accordingly is crucial for compliance.
Common Errors in Filing XBRL Financial Statements
Ensuring the accuracy and consistency of financial statements submitted during the Annual General Meeting (AGM) and in XBRL (eXtensible Business Reporting Language) format is crucial for compliance and transparency. However, several common areas are prone to errors in XBRL reporting. Recognizing and addressing these errors can significantly improve the quality and reliability of financial disclosures.
AGM Financial Statements and Text Block Data in XBRL Format Do Not Match
The content of the text block that comes under “Disclosure of complete set of financial statements” should be identical and legible to the content of your AGM (Annual General Meeting) financial statements. To add the complete set of financial statements in the text block, open the text editor by double-clicking on the text block cell, then copy and paste the full set of financial information from the source document to the text block.
Incomplete XBRL Data
While filing financial statements in XBRL format, you must ensure that all the templates are mentioned in the minimum requirement list. Only those fields that don’t apply to your business should be left blank. The most common errors in the incomplete data include the following fields:-
-
- Share capital
- Property, plant, and equipment
- Employee benefits expense
- Trade receivables
- Other receivables
- Name of parent entity or group
Data in XBRL Financial Statements and AGM Financial Statements Do Not Match
In filing AFS in XBRL format, the XBRL data must match the AGM financial statements. Errors in unmatched data mainly arise from:-
-
- Presentation format (type of income statement)
- Level of rounding (thousands, millions, etc.)
- Earnings per share (EPS) not offered in dollars per share
- Currency indicators (SGD, USD, etc.)
- Type of accounting standards used to prepare AFS (SFRS, SFRS for SE, etc.)
- Incomplete net cash flows
- Profit or loss from discontinued operations (in financial statement highlights)
- Disclosing $0 in the prior year column while preparing consolidated financial statements for the first time, when previous year group level figures are not provided in AGM financial statements

Rounding of Numbers
Differences in rounding numbers can lead to discrepancies between reported figures. It’s essential to maintain consistent rounding policies throughout all financial documents to ensure accuracy and comparability.
Currency Indicators
Mistakes often occur when indicating currencies, especially in multinational operations where multiple currencies are involved. Ensuring that all financial data is correctly converted and reported in the agreed-upon currency is vital for clarity.
Presentation Format
The format in which financial information is presented can vary and lead to confusion. Adhering to the specified presentation formats for XBRL filings ensures that data is uniform and easily interpretable.
The challenge with presentation formats arises because financial information can be displayed in various ways, depending on the accounting standards and practices adopted by a company. This diversity, while reflective of the specific contexts of different businesses, can lead to confusion among stakeholders who need to interpret and compare financial data across companies.
Formatting Issues in XBRL Filing
In xbrl filings, formatting issues can significantly impact the readability and comparability of financial documents. These issues may include inconsistent use of tables, varying fonts and styles for financial figures, and non-uniform application of decimal places and currency formats.
Such inconsistencies make it difficult for investors, regulators, and other users of financial statements to quickly understand and analyze the information presented.
Moreover, the xbrl format allows for financial information to be embedded within HTML documents, enabling the data to be both machine-readable and human-readable.
However, if the presentation format is not carefully managed, the embedded XBRL tags might not accurately reflect the intended financial data, leading to discrepancies between the human-readable and machine-readable layers of the document.
Incomplete Net Cash Flows
Omitting elements of net cash flows can result in an inaccurate portrayal of a company’s liquidity and operational efficiency. Complete and accurate cash flow information is crucial for stakeholders to understand the financial health of the business.
Earnings Per Share (EPS) Formatting
EPS figures must be presented in a consistent format, typically as dollars per share, to allow for straightforward comparison and evaluation by investors and analysts.
Types of Accounting Standards
Discrepancies in the types of accounting standards used, such as IFRS versus SFRS (Singapore Financial Reporting Standards), can lead to significant differences in financial reporting. Consistency in the applied accounting standards is necessary for accurate financial statements.
Profit and Loss from Discontinued Operations
Failure to separately report profit and loss from discontinued operations can obscure the true financial performance of the ongoing operations. Clear disclosure is essential for an accurate understanding of the company’s current and future potential.
First-Time Consolidation Issues
When consolidated financial statements are prepared for the first time, disclosing SGD 0 for the preceding year, without presenting the group’s previous year’s financial data, can mislead stakeholders. It is important to provide comparative information, even if it involves restating the previous year’s figures for consistency with the current year’s consolidation basis.
Incorrect Mapping to XBRL
Map data using the “best-fit” principle, the relevant taxonomy elements in the templates. Use “others” only to classify unique items which cannot be mapped in any other taxonomy element.
Why Choose DataTracks for Error-Free ACRA XBRL Reporting?
You may efficiently use the Singapore ACRA XBRL filing system by following these pointers and best practices. This helps ensure that your business complies with legal obligations. Remember that compliance is essential to preserving good standing and avoiding sanctions.
For companies seeking to navigate the complexities of XBRL ACRA filings confidently, DataTracks offers specialized services designed to facilitate error-free and compliant submissions. Leveraging extensive expertise in XBRL reporting standards and regulatory requirements, DataTracks assists companies in preparing their XBRL filings accurately, ensuring that all data is complete, consistent, and up-to-date with the latest taxonomies and regulatory updates. This professional support helps businesses avoid common pitfalls, streamlining their ACRA compliance processes efficiently.
However, one needs to know that the XBRL filing process is complex, time-consuming, and complicated. This is where we at DataTracks come to your rescue. Our proficient team enables you to streamline and simplify your filing processes. We comprise a team of qualified professionals who develop accurate reports that comply with the XBRL reporting. If you are looking for professional services for XBRL reporting, contact us at DataTracks today. Get in touch with us at +65 31582850 or email us at enquiry@datatracks.com.sg
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some best practices for preparing XBRL Reporting for ACRA filings?
- Start Early: Don’t wait till the last minute. Gather your financial data well in advance to avoid any filing delays.
- Understand the XBRL Taxonomy: Familiarize yourself with the ACRA XBRL taxonomy, which defines the tags and elements used in the filing.
- Use XBRL-compliant software: Investing in XBRL services from a reputable provider like Datatracks can ensure your software adheres to ACRA’s specifications and streamlines the preparation and validation of your XBRL filings.
- Accuracy is key: Double-check your data for accuracy before filing. Errors can lead to rejections and delays.
- Validation is crucial: Ensure your XBRL file is valid before submission using ACRA’s validation tool.
What common mistakes should I avoid when filing my financial statements in XBRL Reporting?
Common pitfalls include incomplete data entry, data inconsistency between XBRL filings and financial statements, incorrect use of taxonomies, overlooking validation errors, failing to update financial statements with the latest data, insufficient review and verification, and ignoring regulatory updates. Avoiding these errors is key to successful XBRL filings.
Can outdated financial statements affect my XBRL reporting process?
Yes, submitting outdated financial statements can result in significant errors. Ensure your filings reflect the most current financial data, compliant with the latest accounting standards and regulatory requirements, to avoid submission errors and potential compliance issues.
How can professional services like DataTracks help with XBRL ACRA filings?
Professional services like DataTracks specialize in XBRL and regulatory reporting, offering expertise to ensure error-free XBRL filings. They can assist with selecting the correct XBRL format, ensuring data completeness and consistency, addressing validation errors, and staying compliant with the latest regulatory updates, simplifying the filing process for companies.


