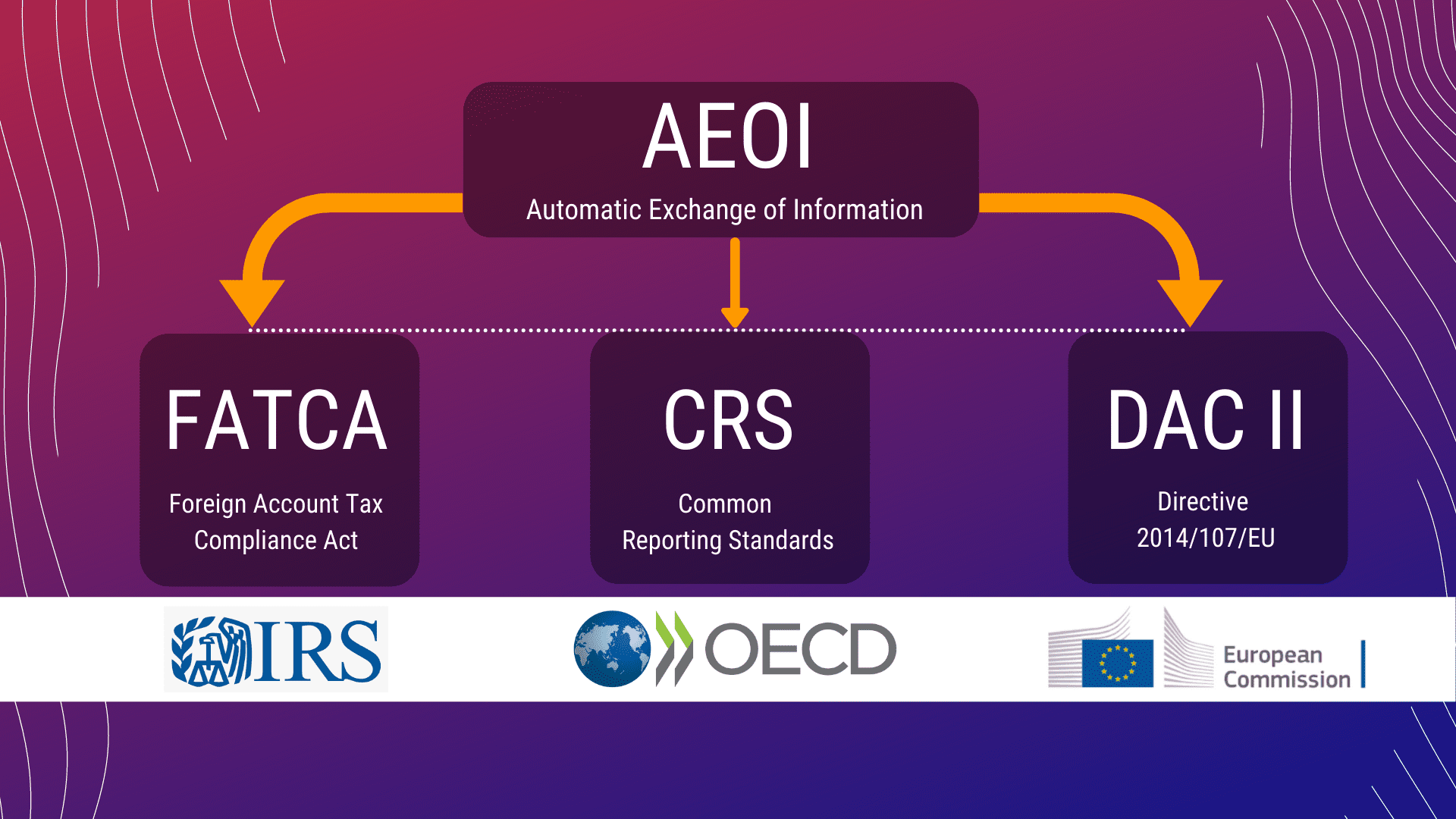
9 things you should know about FATCA
The final version of the Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act (FATCA) was released in January 2013 by the US Department of the Treasury and the Internal Revenue Service. Intended mainly to combat tax evasion, FATCA introduces stringent regulatory and reporting standards. Non-compliance can lead to severe consequences. Here are nine key points to understand about FATCA.
The Cost of Inaction
Tax evasion is a major problem in many countries. It’s estimated that individuals hiding their money in offshore accounts cost the US economy about $100 billion annually. This significant loss highlights the importance of FATCA.
Financial Reclamation
The US government expects FATCA to raise approximately $7.6 billion for the IRS in tax revenue over ten years. This substantial figure underscores the law’s role in reclaiming lost tax revenue.
Comprehensive Mandates
FATCA mandates foreign financial institutions to register with the IRS and report information on accounts held by US clients offshore. It operates by collecting relevant tax information on US citizens holding accounts abroad, ensuring thorough compliance.
Extensive Reach
FATCA applies globally to any financial institution associated with US clients holding over fifty thousand dollars in their accounts. This includes banks, fund managers, and custody banks, covering any entity with US clients in its books.
Severe Penalties
Non-compliance with FATCA carries heavy penalties. As of December 2013, penalties included a 30% withholding tax on new accounts or contracts for non-registration. General withholding requirements began in January 2014, with non-compliance resulting in a 30% withholding of any US client’s income.
Applicability
FATCA applies to account holders of offshore institutions associated with US taxpayers or clients required to pay taxes in the US. This broad applicability ensures that all relevant entities comply with reporting standards.
Operational Requirements
Inter-Governmental Agreements (IGAs) facilitate compliance for financial institutions. There are two IGA models: one where institutions report directly to the IRS, and another where institutions report to their country’s government, which then shares the information with the IRS.
Sub-Funds Ambiguity
Currently, there are no clear guidelines regarding sub-funds under FATCA. It remains unclear whether the umbrella fund suffices or if each sub-fund must be registered individually. Consultants note that the IRS and the Treasury have yet to provide clarity on this matter.
Impact on Gold Values
Censuring offshore accounts may have long-term effects on the market, potentially causing the removal of US securities from foreign institutions. Such large drops in investment dollars could lead to a market crash, devaluing the USD. Consequently, this scenario could lead to a rise in the value of gold.
Understanding these nine aspects of FATCA is crucial for financial institutions and individuals alike, as compliance ensures the avoidance of severe penalties and contributes to the global fight against tax evasion.
If you need any sort of help with FATCA Reporting DataTracks has just what you need. With features ranging from flexible data entry to version history and audit trails, no matter what you’re looking for concerning FATCA or CRS regulations, DataTracks can help.
Navigating the complexities of FATCA compliance can be daunting, but with DataTracks’ FATCA CRS reporting software, financial institutions can achieve seamless compliance with ease. By automating the collection and reporting processes, ensuring accuracy, and providing robust support, DataTracks stands out as a reliable partner in helping institutions meet their regulatory obligations. Embrace the power of DataTracks’ FATCA reporting software to mitigate risks, avoid severe penalties, and contribute to a transparent and compliant financial ecosystem.